Bonjour, comment pouvons-nous vous aider ?
ChatGPT was developed by OpenAI, an artificial intelligence research laboratory consisting of the for-profit corporation OpenAI LP and its parent company, the non-profit OpenAI Inc. The team at OpenAI developed the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture, which is the foundation of ChatGPT. While there were many individuals involved in the development of ChatGPT, the team at OpenAI is credited with its invention.
In this blog post, we will discuss the pro’s and cons of how ChatGPT tools can help individuals in their daily lives.
In recent years, the field of artificial intelligence has made significant strides in developing natural language processing (NLP) capabilities. One of the most impressive developments in this field is the emergence of conversational AI, which enables machines to engage in human-like dialogue.
ChatGPT, a large language model trained by OpenAI based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, is one such example of conversational AI. With its advanced natural language processing capabilities, ChatGPT is able to understand and respond to a wide range of queries posed in natural language.
ChatGPT has been trained on a massive corpus of text data, which includes everything from news articles to social media posts to literature. This vast training data has enabled ChatGPT to develop a deep understanding of the nuances of human language, allowing it to generate human-like responses to a wide range of questions.
One of the key benefits of ChatGPT is its versatility. It can be used for a wide range of applications, including customer service, personal assistance, and even creative writing. ChatGPT can also be integrated with a variety of platforms, including websites, messaging apps, and voice assistants, making it highly flexible and adaptable.
In addition to its versatility, ChatGPT is also highly scalable. Because it is an AI-based solution, it can handle a large volume of queries simultaneously, allowing businesses to efficiently manage large volumes of customer inquiries without having to invest in additional resources.
While Chat GPT can generate text that is similar to what a human copywriter might produce, it is not designed to replace human copywriters entirely. There are several reasons for this.
Firstly, Chat GPT is a machine learning algorithm, and while it can produce high-quality text, it does not have the same level of creativity or insight that a human copywriter can bring to a project. A human copywriter can think beyond the parameters of the data fed into the machine and can use their intuition, experience, and creativity to come up with unique and compelling ideas.
Secondly, Chat GPT is limited by the data it has been trained on. It can only produce text based on the data it has been fed, which means it may struggle with producing content on subjects that are outside of its training data.
Finally, copywriting involves more than just generating text. It requires an understanding of marketing strategy, brand voice, and audience targeting, as well as the ability to collaborate with other members of a marketing team. These are skills that are difficult for a machine to replicate.
In summary, Chat GPT is a powerful tool that can assist copywriters in their work, but it is unlikely to replace them entirely.
Chat GPT is a machine learning model that is designed to generate human-like responses to text-based input. While the technology has many potential applications, including in customer service, content creation, and language translation, there are also ethical implications to consider.
One of the primary concerns with Chat GPT is the potential for it to be used to spread misinformation or propaganda. The model is capable of generating convincing fake news articles or social media posts that could be used to manipulate public opinion or spread false information. This could have serious consequences for democracy, public safety, and individual privacy.
Another ethical concern is the potential for Chat GPT to perpetuate biases and stereotypes. The model is trained on large datasets of text, which can reflect the biases and prejudices of the people who created the data. If these biases are not addressed, the model may generate responses that perpetuate harmful stereotypes or discriminate against certain groups of people.
Additionally, there are concerns about the impact of Chat GPT on the job market. As the technology becomes more advanced, it could replace human workers in certain industries.
To mitigate these ethical concerns, it is important for developers and users of Chat GPT to prioritise transparency and accountability. This could include measures such as providing clear disclaimers when Chat GPT is being used, implementing safeguards to prevent the spread of misinformation, and regularly auditing the model to identify and address biases.
In conclusion, while Chat GPT has the potential to revolutionise many industries, it is important to consider the ethical implications of its use. By prioritising transparency and accountability, we can help ensure that the technology is used in a responsible and ethical manner.
ChatGPT is revolutionising the way businesses engage with their customers. Its cutting-edge natural language processing abilities, scalability, and versatility make it a top choice for conversational AI. However, it’s important to note that ChatGPT is not here to replace the art of brand copywriting, which remains a uniquely human skill. Instead, it can work hand-in-hand with copywriters to enhance and optimise customer interactions, leading to even greater success for businesses.”
Author – Pete Bucheler
Around 60% of the global population uses the internet, seeing a 20% increase in the past two years with many businesses forced to shut their physical doors and migrate online. Although it may seem like there is increased competition, the main advantage of digital marketing is that a targeted audience can be reached in a cost-effective and measurable way than traditional advertising. Many business owners, however, still struggle to master the fundamentals of digital marketing – not surprising since there is a wide range of digital marketing services, such as search engine optimisation (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), content marketing, and social media marketing to name a few.
Working with an expert can not only help you reach your target audience but also increase brand loyalty and drive online sales.Consider partnering with Ideas Marketing named one of the best Australian digital marketers to consider partnering with in 2022.
Ideas Marketing is proud to be named 20 Australian Digital Marketers to work with from the Australian Business Journal
See our write up below


It all starts with ideas. A strategy first branding agency, [ideas] Marketing Agency is where your ideas are born and brought to life. Founded by Scott Bouquet in 2016, the [ideas] team are brand marketing experts and career professionals here to develop your company’s branding and marketing communications with innovative and strategic thinking.
Working alongside clients, the process begins with implementing solid foundations of strategy, followed by critical marketing and branding disciplines, including design, print, digital and promotion. “Our goal is to build partnerships with clients using clear and concise communication from your team to ours,” says Scott.
“With clients’ best interests in mind, [ideas] Marketing has been deliberately structured to provide small businesses in Australia with the highest value. Small to medium-sized enterprises (SME’s) can receive ongoing branding and marketing support on-demand as the team and resources have been carefully curated. [ideas] Marketing was created to bring ideas to life and do good for businesses and the people behind them.”
In today’s world, marketing has become more complex than ever before. With the ever-increasing competition in the market, it is crucial for companies to stay ahead of the curve and understand the needs and desires of their target audience. This is where neuromarketing comes in. A field that combines the principles of marketing and neuroscience to understand consumer behaviour and decision-making processes.
It’s the study of how consumers respond to marketing stimuli at the subconscious level. It involves using techniques such as brain imaging, eye-tracking, and biometric measurements to understand how consumers react to various marketing messages and stimuli. By understanding the inner workings of the brain, marketers can create more effective and persuasive marketing campaigns. It will resonate with the correct target audience.
One of the main benefits of neuromarketing is the ability to gain insights into the subconscious mind of consumers. Traditional marketing methods rely on self-reported data from consumers, which can often be inaccurate or biased. Neuromarketing on the other hand, provides objective data on how consumers react to various marketing stimuli. This will including their emotional responses, attention levels, and decision-making processes.
Another benefit of this is the ability to create more effective marketing campaigns. By understanding the neural mechanisms that underlie consumer behaviour, marketers can create messages and campaigns that resonate with their target audience at a subconscious level. This can lead to higher engagement, increased sales, and stronger brand loyalty.
The techniques include a range of tools and methods that are used to understand the brain’s response to marketing stimuli. Some of the most used techniques include: Brain Imaging, Eye-tracking, Biometric Measurements, Surveys and questionnaires. below we dive in to each of these in more detail.
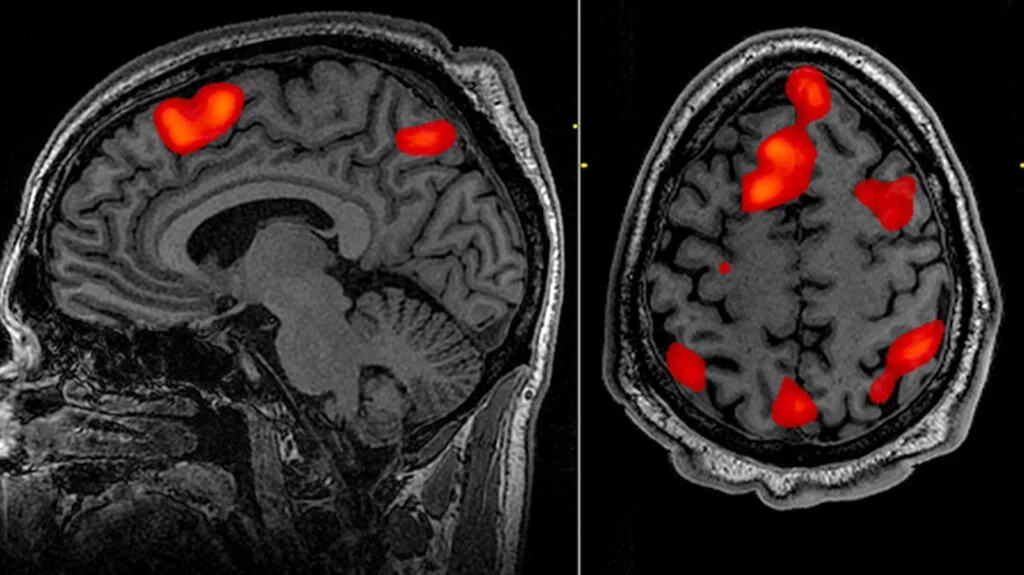

This involves using techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brain activity in response to marketing stimuli.
fMRI measures changes in blood flow to different regions of the brain, allowing researchers to identify which areas are active during specific tasks or stimuli. In neuromarketing, fMRI is often used to measure consumers’ responses to marketing materials, such as advertisements or product packaging. By analysing brain activity patterns in response to these stimuli, marketers can gain insights into which elements are most engaging or persuasive to consumers.
EEG measures emotional responses to marketing materials, while fMRI and EEG have their strengths and limitations in neuromarketing research. Both techniques provide insights into neural processes underlying consumer behaviour.


Using special cameras to track the movement of a person’s eyes as they view marketing messages or products.
There are two main types of eye tracking: remote and wearable. Remote eye tracking uses cameras and infrared sensors to track the movement of the eyes from a distance, while wearable eye tracking involves placing small cameras or sensors directly on the eyes or eyeglasses.
In neuromarketing research, eye tracking can provide valuable insights into how consumers engage with different types of marketing materials. For example, by tracking where consumers look on an advertisement or website, researchers can identify which elements attract the most attention and how consumers navigate through the content.
Eye tracking can also reveal subconscious responses to marketing stimuli. For example, by measuring the amount of time consumers spend looking at certain images or text, researchers can infer which elements are most engaging or persuasive, even if the consumer is not consciously aware of it.
Overall, eye tracking provides a powerful tool for neuromarketers to understand how consumers engage with marketing materials and make decisions. By combining eye tracking with other neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI or EEG, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the neural processes underlying consumer behaviour.


Measuring physical responses such as heart rate, skin conductance, and facial expressions in response to marketing stimuli.
HRV and skin conductance are biometric measurements used in neuromarketing research to identify emotionally engaging marketing stimuli. Facial expressions are also used to identify positive or negative emotional responses. These measurements provide valuable insights into consumer behavior and can be combined with other techniques to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the processes underlying it.


Although traditional marketing research methods are often unreliable, they can still be useful when combined with neuromarketing techniques. Surveys and questionnaires can provide valuable insights into consumer attitudes and beliefs.
To better understand consumer behaviour, marketers often use surveys and questionnaires along with other neuromarketing techniques. Combining surveys with fMRI or EEG measurements provides insights into consumer behaviour.
Using surveys and questionnaires in conjunction with other neuromarketing techniques can enhance marketers’ understanding of consumer behaviour. This is useful for assessing consumers’ recall of marketing messages and gaining additional context about the stimuli presented. Employing a range of techniques can lead to more effective marketing campaigns.
Overall, surveys and questionnaires provide a valuable tool to gather information on consumers’ attitudes, beliefs, and preferences. Combining surveys with other neuromarketing techniques provides a more complete understanding of consumer behaviour.
There are several ethical implications to consider when it comes to using these techniques.
Invasion of privacy: Neuromarketing involves measuring brain activity in response to marketing stimuli, which may include sensitive personal information. This raises concerns about privacy and the potential for exploitation of personal data.
Manipulation: By tapping into consumers’ subconscious minds, neuromarketing techniques have the potential to manipulate consumers’ behaviour and decision-making. This raises concerns about this technology. Companies must prioritise ethical practices when using neuromarketing to ensure that it is in line with the best interests of their customers.
Informed consent: It is important that individuals who participate in these studies are fully informed about the nature of the research and how their data will be used. This includes ensuring that individuals have given their informed consent before participating in studies. Also, that they are aware of their right to withdraw from the study at any time.
Transparency:To ensure ethical neuromarketing practices, companies should be transparent about their methods and provide clear information to customers about research methods and data usage. This builds trust and can lead to greater brand loyalty and engagement.
In summary, businesses that utilise neuromarketing techniques must take into account the ethical implications of this technology. Moreover, it is crucial to ensure that they utilise the technology responsibly and ethically. Additionally, companies must be transparent with consumers about their methods and how their data will be used to establish trust and foster a positive relationship that can lead to greater brand loyalty and engagement.
Our team used a specialised camera to track participants’ eye movements as they viewed different ads, collecting valuable data on which parts of the ad were most and least engaging. Using this data, we optimised the ad’s design and content for maximum effectiveness.
The study identified the most effective ad for Propertybuyer’s campaign,” said Scott Bouquet.




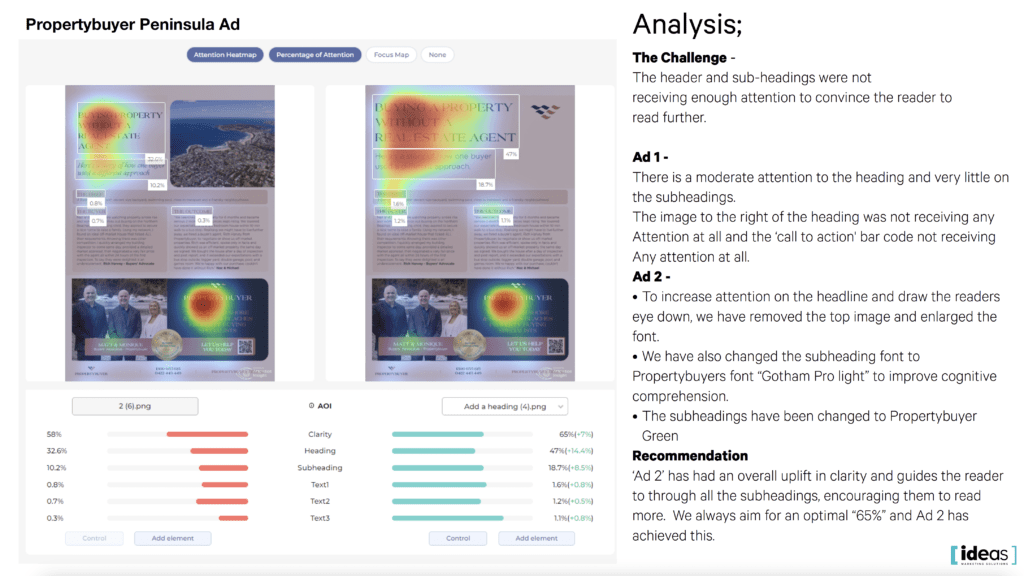

Neuromarketing combines marketing and neuroscience to gain insights into consumer behaviour and decision-making. Neuromarketing helps marketers create effective campaigns by understanding how the brain responds to marketing stimuli. As technology advances, neuromarketing’s potential applications will continue to grow, making it an essential tool for staying competitive.
As the Director of Ideas Marketing, I’ve seen firsthand how neuromarketing can impact campaign success. Using techniques like brain imaging, eye tracking, and biometric measurements, we gain deeper insights into consumer responses to our marketing.
However, it’s important to note that neuromarketing is not a magic bullet for marketing success. To fully understand consumer behaviour, companies should combine these methods with other marketing research tools, such as surveys and focus groups said Scott Bouquet.
In conclusion, I believe that neuromarketing is a powerful tool that has the potential to revolutionise the way we think about marketing. By harnessing the power of the human brain, we can create more engaging and effective marketing campaigns that truly resonate with our target audience. As the field continues to evolve, I look forward to seeing how it will continue to shape the future of marketing.
Author: Scott Bouquet


This site is not available in landscape mode,
Please turn your mobile.
Bonjour, comment pouvons-nous vous aider ?